
On sweet glands, salivary glands, and intestinal cells.Īldosterone increases the reabsorption of sodium and the secretion of potassium by the ducts, The effect on the sweat glands is important to conserve body salt in hot environments and the effect on the salivary glands is necessary to conserve salt when excessive quantities of saliva are lost, Aldosterone also greatly enhances sodium absorption by the intestines, which obviously prevents the loss of sodium in the stools.

abundant sER, mitochondria with tubular cristae, and numerous lipid droplets.
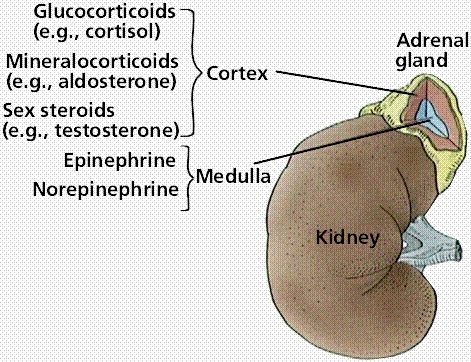
Function: the cells secrete mineralocorticoids, mainly aldosterone. sER, mitochondria with tubular cristae, and few lipid droplets.

The cells are columnar or pyramidal in shape with dense nuclei and slightly vacuolated eosinophilic cytoplasm.īy EM: the cells show the ultrastructural features of steroid secreting cells i.e.The cells are arranged in closely-packed arched clusters surrounded by fenestrated blood capillaries.It lies immediately under the connective tissue capsule, forming 15% of the cortex.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
